Table of Contents
IRS Form 5498-ESA – Coverdell ESA Contribution Information – If you’re saving for your child’s education through a Coverdell Education Savings Account (ESA), understanding IRS Form 5498-ESA is crucial. This form tracks contributions to these tax-advantaged accounts, helping the IRS ensure compliance with annual limits and eligibility rules. As we head into the 2025 tax year, staying informed about Form 5498-ESA can prevent penalties and maximize your education savings benefits. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll break down what Form 5498-ESA is, who needs it, filing deadlines, and tips for 2025—drawing from the latest IRS guidelines.
What Is a Coverdell ESA?
A Coverdell ESA is a tax-advantaged savings account designed to help families cover qualified education expenses for a designated beneficiary, typically a child under age 18 (or any age for special needs beneficiaries). Unlike 529 plans, which focus heavily on higher education, Coverdell ESAs offer flexibility for K-12 costs like tuition, books, supplies, tutoring, and even uniforms or transportation at eligible elementary, secondary, or postsecondary institutions.
Contributions are made with after-tax dollars and aren’t deductible, but earnings grow tax-deferred, and qualified withdrawals are tax-free. This makes Coverdell ESAs a powerful tool for long-term education planning, especially when combined with other benefits like the American Opportunity Credit or Lifetime Learning Credit.
What Is IRS Form 5498-ESA?
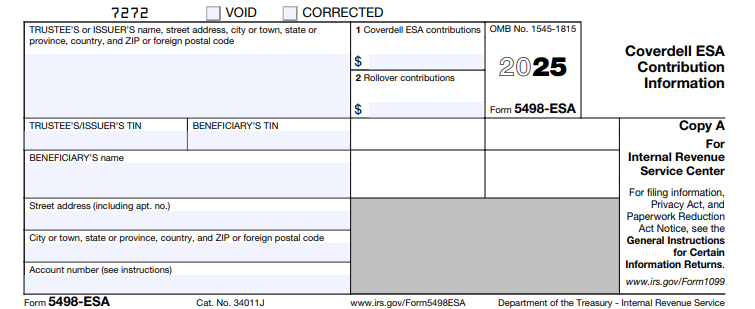
IRS Form 5498-ESA, titled “Coverdell ESA Contribution Information,” is an informational tax form used to report annual contributions to a Coverdell ESA. Filed by the account trustee or custodian (such as a bank, credit union, or brokerage firm), it provides the IRS and the account beneficiary with a record of deposits, including regular contributions and rollovers. This ensures contributions stay within IRS limits and helps beneficiaries track their basis for future tax-free distributions.
Unlike Form 1099-Q (which reports distributions), Form 5498-ESA focuses solely on inflows. It’s not attached to your personal tax return but is essential for verifying eligibility for tax benefits and avoiding excise taxes on excess contributions.
Key Boxes on Form 5498-ESA for 2025
The 2025 version of Form 5498-ESA includes minimal changes from prior years, primarily updating the tax year and adding a reference URL for general instructions. Here’s a breakdown of the main reporting fields:
| Box | Description | What It Reports |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Contributions (Other Than Amounts in Box 2) | Total non-rollover contributions made from January 1, 2025, through April 15, 2026, designated for the 2025 tax year. Includes cash contributions but excludes rollovers. |
| 2 | Rollover Contributions | Any rollover amounts, including trustee-to-trustee transfers or military death gratuities, received in 2025. These are tax-free if properly executed. |
| 3 | Roth IRA Conversions | N/A for Coverdell ESAs (reserved for IRA forms). |
| 4 | Fair Market Value | The value of the ESA as of December 31, 2025, for IRS tracking. |
| 5 | Postsecondary Tuition | Indicates if contributions were used for qualified postsecondary expenses (informational only). |
Trustees must also include the beneficiary’s name, address, and Taxpayer Identification Number (TIN). An account number is encouraged for easier tracking.
Who Must File Form 5498-ESA?
Financial institutions acting as trustees or custodians must file Form 5498-ESA for every Coverdell ESA they maintain during the year, even if no contributions were made—unless it was a total distribution with no inflows. This includes banks, brokerages, and approved entities.
Beneficiaries (or their guardians) receive a copy but don’t file the form themselves. Instead, use it to confirm contributions on your tax records. If you’re self-directed or using a non-traditional custodian, ensure they comply to avoid IRS notices.
Filing Deadlines and Requirements for 2025
Timely filing is key to IRS compliance. For the 2025 tax year:
- Furnish to Beneficiary: By April 30, 2026. This gives you time to review before your tax return deadline.
- File with IRS: By June 2, 2026 (extended from May 31 due to weekends/holidays). E-filing is mandatory for 10+ forms; paper filing is allowed for fewer.
- Electronic Filing Threshold: Reduced to 10 returns under the Taxpayer First Act.
Use the IRS’s FIRE system for e-filing, and include Form 1096 as a transmittal summary. Corrections can be filed anytime, but aim for accuracy to avoid penalties (up to $310 per form for late filing).
IRS Form 5498-ESA Download and Printable
Download and Print: IRS Form 5498-ESA
Contribution Limits and Rules for Coverdell ESAs in 2025
To stay compliant, contributions must adhere to strict IRS rules—no changes for 2025.
- Annual Limit: $2,000 per beneficiary (across all ESAs), regardless of the number of contributors. Excess amounts (plus earnings) must be withdrawn by June 1, 2026, to dodge a 6% excise tax.
- Deadline: Contributions for 2025 can be made from January 1, 2025, to April 15, 2026 (tax filing deadline, no extensions). Designate the year when contributing post-December 31.
- Income Limits (MAGI Phaseout): Full $2,000 if MAGI is under $95,000 (single) or $190,000 (joint). Phaseout between $95,000–$110,000 (single) or $190,000–$220,000 (joint). No contributions above $110,000/$220,000. Use IRS Worksheet 6-1 in Publication 970 to calculate.
- Eligible Contributors: Anyone (individuals, family, friends) meeting income rules; cash only. No contributions after beneficiary turns 18 (except special needs).
- Rollovers: Allowed once per 12 months to another ESA for the beneficiary or family member under 30; report in Box 2.
| Filing Status | Full Contribution MAGI Limit | Phaseout Range |
|---|---|---|
| Single/Head of Household | Under $95,000 | $95,000–$110,000 |
| Married Filing Jointly | Under $190,000 | $190,000–$220,000 |
Common Mistakes to Avoid with Form 5498-ESA
- Missing the Designation: Post-2025 contributions must specify the tax year; otherwise, they’re applied to 2026.
- Overlooking Excess Contributions: Track total inflows across all ESAs—use Form 5329 for penalties.
- TIN Errors: Verify the beneficiary’s SSN to prevent rejections.
- Ignoring FMV Reporting: Box 4 helps with basis calculations for distributions.
- Late Beneficiary Copies: Delays can complicate your tax prep.
Tools like TaxBandits or 1099FIRE can automate audits and e-filing for trustees.
How Form 5498-ESA Ties Into Your Taxes
While you don’t attach Form 5498-ESA to Form 1040, it supports:
- Verifying tax-free status on Form 1099-Q distributions.
- Claiming education credits (expenses can’t double-dip with ESA withdrawals).
- Reporting excess contributions on Form 5329.
Qualified distributions reduce adjusted qualified education expenses (AQEE) for credits, per IRS Publication 970. Non-qualified withdrawals incur income tax plus a 10% penalty on earnings.
Final Thoughts: Maximize Your 2025 Coverdell ESA with Form 5498-ESA
IRS Form 5498-ESA is more than paperwork—it’s your roadmap to compliant, tax-efficient education savings. With the $2,000 limit unchanged for 2025 and flexible K-12 uses, Coverdell ESAs remain a smart complement to 529 plans for families. Review your statements by May 2026, and consult a tax pro if your MAGI nears phaseout levels.
For the latest forms and pubs, visit IRS.gov/Form5498ESA or download Publication 970. Start contributing early—your child’s future education depends on it!
This article is for informational purposes only and not tax advice. Consult a qualified professional for personalized guidance.