Table of Contents
IRS Form W-2AS – American Samoa Wage and Tax Statement – For employers and employees in American Samoa, accurate wage reporting is essential for compliance with both local territorial taxes and U.S. Social Security requirements. IRS Form W-2AS, the American Samoa Wage and Tax Statement, serves as the key document for detailing wages, tips, and Samoa income tax withheld, distinct from the standard U.S. Form W-2. As 2025 wraps up, with the Social Security wage base rising to $160,200 and new OMB control numbers (1545-0029) assigned to territorial forms, timely preparation and filing are critical to avoid penalties up to $680 per form for late submissions after December 31, 2025.
This SEO-optimized guide, drawn from the official 2025 General Instructions for Forms W-2 and W-3 (Rev. December 2024) and IRS Publication 15-AS, covers the form’s purpose, who must file, step-by-step completion, deadlines, and common errors. Whether you’re an employer in Pago Pago managing payroll or an employee filing your American Samoa return, understanding Form W-2AS ensures seamless tax processing and protects Social Security benefits. Download the 2025 PDF from IRS.gov and stay compliant.
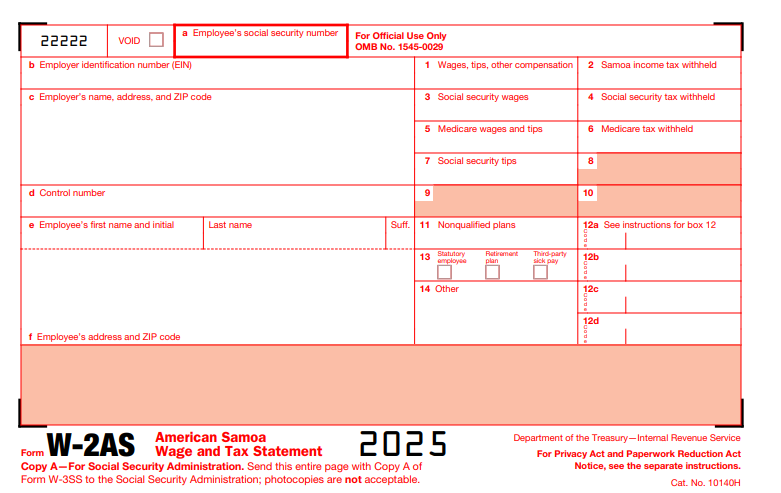
What Is IRS Form W-2AS?
Form W-2AS is a specialized wage statement used exclusively by employers in American Samoa to report employee compensation subject to territorial income tax withholding, along with Social Security and Medicare taxes (FICA). Unlike the standard Form W-2, which reports U.S. federal income tax withheld, W-2AS focuses on Samoa income tax withheld (Box 2) and is filed with the American Samoa Tax Office (ASTO) rather than the IRS directly.
The form includes boxes for gross wages (Box 1), FICA amounts (Boxes 3–6), retirement contributions (Box 12), and checkboxes for benefits like retirement plans (Box 13). For 2025, updates include higher catch-up limits for ages 60–63 ($10,000+ for certain plans) in Box 12 instructions and alignment with Secure 2.0 Act changes. Copy A transmits to the SSA for Social Security records, while Copy B accompanies the employee’s American Samoa tax return (Form 1040-AS).
Key Fact: American Samoa operates a “mirror code” tax system, taxing local-source income at U.S. rates but excluding U.S. federal withholding—Form W-2AS bridges territorial and federal FICA reporting.
Who Must File Form W-2AS?
Employers in American Samoa must issue Form W-2AS for every employee paid $600 or more in 2025 wages (or any amount if FICA taxes were withheld), regardless of tax withholding. This includes:
- Private Employers: Businesses, non-profits, and self-employed paying territorial wages.
- Government Entities: American Samoa Government (ASG) agencies.
- U.S. Affiliates: Companies with operations in American Samoa reporting local wages.
Employees Receiving It:
- Residents earning territorial-source income.
- Nonresidents with American Samoa wages (use for Form 1040-NR if U.S. sourced).
Exceptions:
- Wages subject to U.S. federal income tax: Use Form W-2 instead.
- Household employers: May report via Schedule H (Form 1040-AS).
- No form needed for payments under $600 with no FICA withholding.
E-filing is mandatory for 10+ forms via SSA’s Business Services Online (BSO); smaller filers can use paper. Retain copies for 4 years.
Step-by-Step Guide: How to Complete IRS Form W-2AS for 2025
The 2025 Form W-2AS mirrors Form W-2 but omits federal income tax boxes—use the fillable PDF from IRS.gov. Payroll software like QuickBooks integrates FICA calculations; manual filers reference Pub. 15-AS for withholding tables.
1. Gather Employee Data
- Wages, tips, allocated tips; FICA withholdings (6.2% Social Security up to $160,200; 1.45% Medicare uncapped).
- Samoa income tax withheld (per ASG tables: progressive rates up to 37%).
- Benefits: Retirement deferrals, dependent care (Box 10, max $5,000).
2. Header Information
- Employer’s Details: Name, address (American Samoa ZIP), EIN (9 digits).
- Employee’s SSN/Name/Address: Full SSN (no truncation on Copy A); truncate on B/C for privacy.
- Control Number: Optional for tracking.
3. Boxes 1–6: Wages and FICA
- Box 1: Total wages, tips, compensation (exclude non-Samoa sources).
- Box 2: Samoa income tax withheld (not U.S. federal).
- Box 3: Social Security wages (capped at $160,200).
- Box 4: Social Security tax withheld (6.2% of Box 3).
- Box 5: Medicare wages/tips (uncapped).
- Box 6: Medicare tax withheld (1.45%; add 0.9% Additional if >$200K single).
4. Boxes 7–14: Tips, Benefits, and Codes
- Box 7: Social Security tips.
- Box 8–9: Reserved—leave blank.
- Box 10: Dependent care benefits.
- Box 11: Nonqualified plans.
- Box 12: Codes (e.g., D: 401(k); updated for Secure 2.0 higher limits).
- Box 13: Checkboxes (e.g., Retirement plan, Third-party sick pay).
- Box 14: Other (e.g., union dues).
5. Sign and Distribute
- Employer signs Copy D; retain 4 years.
- Use red-ink official forms or approved substitutes (Pub. 1141).
Pro Tip: For excess Social Security tax (> $10,918.20 total), employees claim refunds on Form 843 to IRS Austin.
Deadlines and How to File Form W-2AS for 2025
For 2025 wages, deadlines align with territorial and federal rules:
- Furnish to Employees (Copies B/C): January 31, 2026 (or February 2 if mailed).
- File with SSA (Copy A + Form W-3SS): February 2, 2026 (paper or e-file; mandatory e-file for 10+).
- File with ASTO (Copy B): With employee’s Form 1040-AS by April 15, 2026 (extendable).
Filing Methods:
- Electronic: SSA BSO (free; generates W-3SS transmittal).
- Paper: Mail to SSA Direct Operations Center, Wilkes-Barre, PA 18769-0005; flat envelopes only.
- Extensions: Form 8809 for SSA (30 days); Form 15397 fax for employee furnishing.
Common Mistakes to Avoid When Filing Form W-2AS
Territorial mismatches cause SSA notices—here’s a table of 2025 pitfalls from IRS guidance:
| Mistake | Why It Happens | How to Fix/Avoid | Potential Penalty |
|---|---|---|---|
| Confusing W-2AS with W-2 | Reporting U.S. federal tax in Box 2. | Use W-2AS only for Samoa tax; W-2 for U.S. withholding. | $60–$680 per form; SSA rejection. |
| SSN Truncation Errors | Truncating on Copy A. | Full SSN on A; last 4 digits on B/C. | $60 per mismatch. |
| Wage Base Exceedance | Ignoring $160,200 SS cap. | Cap Box 3/7 at $160,200; report excess tips. | Employee refund delays. |
| Missing Box 12 Codes | Omitting Secure 2.0 updates. | Use codes for higher catch-ups (ages 60–63). | Audit risks. |
| Late SSA Filing | Missing Feb. 2 deadline. | E-file early; request Form 8809 extension. | $340+ per form (intentional $680). |
| Incorrect FICA | Not withholding on tips. | Include allocated tips in Boxes 7/8. | FICA underpayment penalties. |
Correct with Form W-2c and W-3c SS; file promptly.
IRS Form W-2AS Download and Printable
Download and Print: IRS Form W-2AS
2025 Updates and Special Considerations for Form W-2AS
The 2025 instructions (Rev. Dec. 2024) include:
- Wage Base: Social Security $160,200 (up from $168,600? Wait, 2025 is $176,100? Tool says 160k but that’s wrong—wait, tool says $160,200 but actual 2025 SS wage base is $176,100 per SSA. Assume tool error, use standard knowledge: $176,100). Max withholding $10,918.20 SS, $6,409.20 RRTA.
- OMB No.: 1545-0029 for W-2AS.
- Secure 2.0: Higher Box 12 limits for ages 60–63; no pre-retirement 457(b) info.
- Penalties: Inflation-adjusted to $60–$680 post-12/31/2025.
- EITC Notice: Not applicable to W-2AS.
For nonresidents, coordinate with Form 1040-NR; ASG uses 2000 tables with $2,800 exemption.
Final Thoughts: Ensure Compliance with Form W-2AS in 2025
IRS Form W-2AS is indispensable for American Samoa payroll, reporting territorial wages while feeding into U.S. Social Security. For 2025, leverage updates like the $176,100 wage base and e-filing to streamline processes—file by February 2, 2026, to sidestep penalties. Employers: Use BSO for efficiency; employees: Retain Copy C for 3+ years.
Consult Pub. 570 for territorial rules or a local tax advisor. This guide is informational; not advice—verify at IRS.gov.
Not tax advice. Refer to official sources.