Table of Contents
IRS Form 1099-Q – Payments from Qualified Education Programs (Under Sections 529 and 530) – Saving for education through tax-advantaged accounts like 529 plans or Coverdell Education Savings Accounts (ESAs) can provide significant benefits, but withdrawals require careful tracking to avoid unexpected taxes or penalties. IRS Form 1099-Q—Payments from Qualified Education Programs (Under Sections 529 and 530)—is the key document that reports these distributions, helping the IRS and recipients determine if earnings are taxable. For tax year 2025, with expanded qualified expenses under the One Big Beautiful Bill Act (e.g., up to $20,000 for K-12 tuition starting in 2026, but $10,000 in 2025), Form 1099-Q ensures compliance amid rising 529 assets exceeding $500 billion. This SEO-optimized guide, based on the latest IRS instructions (Rev. April 2025), covers filing requirements, tax implications, and common pitfalls to maximize your education savings.
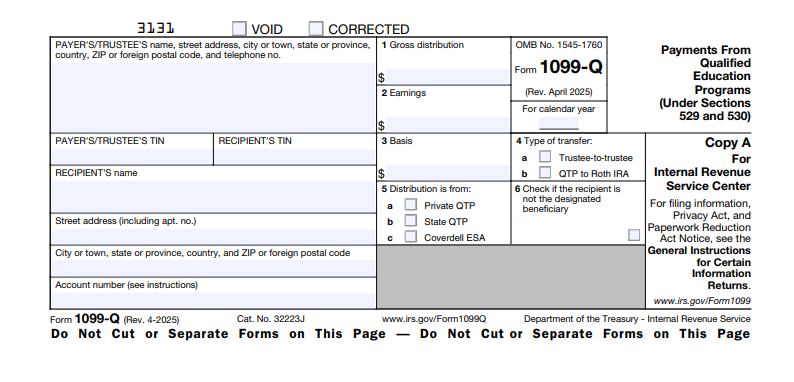
What Is IRS Form 1099-Q?
IRS Form 1099-Q reports distributions from qualified tuition programs (QTPs), including 529 plans and Coverdell ESAs, under IRC Sections 529 and 530. Issued by program trustees or payers (e.g., state agencies or financial institutions), it breaks down gross distributions, earnings, and basis to calculate any taxable portion. Earnings grow tax-free, but non-qualified withdrawals trigger ordinary income tax on earnings plus a 10% penalty.
Key features:
- Recipient Focus: Sent to the designated beneficiary (student) or account owner (e.g., parent) if the owner receives the funds.
- Tax Calculation Aid: Box 2 (earnings) minus qualified expenses determines taxable amount; no reporting needed for fully qualified distributions.
- Roth Rollover Support: Reports transfers to Roth IRAs (up to $35,000 lifetime limit, $7,000 annual for under-50s in 2025).
The April 2025 revision (Cat. No. 32223J) includes online fillable formats due to low paper volume and aligns with e-filing thresholds. Download the form and instructions from IRS.gov/Form1099Q.
Who Needs to File IRS Form 1099-Q in 2025?
Payers must file if they made any distribution from a 529 plan or Coverdell ESA in 2025, regardless of amount or taxability. Recipients use it to report on Form 1040.
| Role | Filing/Reporting Requirement |
|---|---|
| Payers/Trustees | File for every distribution; e-file if 10+ info returns (aggregated). |
| Designated Beneficiary | Report taxable portions on Form 1040, Schedule 1, line 8r; penalty on Schedule 2, line 8. |
| Account Owner | Report if receiving non-direct distribution; rollover to Roth treated as distribution. |
| No Distribution | No Form 1099-Q issued; internal transfers/rollovers exempt. |
Even qualified distributions generate the form—recipients calculate taxability using Pub. 970. Nonresident aliens may require ITINs.
Filing Deadlines and Submission for Form 1099-Q
Timely filing avoids penalties up to $310 per form. Deadlines for 2025 distributions (reported in 2026):
| Deadline | Date | Details |
|---|---|---|
| Furnish to Recipient (Copy B) | January 31, 2026 | Mail or electronic; include Pub. 970 summary. |
| File with IRS (Copy A) | February 28, 2026 (paper) or March 31, 2026 (e-file) | Use Form 1096 transmittal; e-file via IRIS system. |
| Extensions | Automatic 30 days via Form 8809 (by original due date) | For IRS only; furnish to recipients on time. |
- E-Filing: Required for 10+ returns; optional otherwise via IRS-approved software.
- Where to File: Paper to IRS at addresses in Pub. 1220; e-file through FIRE/IRIS.
- Corrections: File amended forms promptly; no penalty for inconsequential errors.
For 2025, low paper volume means online fillable forms are encouraged.
Step-by-Step Guide to Completing IRS Form 1099-Q
Payers use the April 2025 fillable PDF; recipients reference it for taxes. Gather distribution records, TINs, and expense details.
- Payer Info: Enter name, EIN, address; optional account number for multiples.
- Recipient (Boxes 1–3): Name, address, TIN of beneficiary (if direct) or owner (if indirect).
- Gross Distribution (Box 1): Total paid, including earnings and basis.
- Earnings (Box 2): Taxable portion; $0 if fully qualified.
- Basis (Box 3): Nontaxable contributions returned.
- Trustee-to-Trustee Rollover (Box 4): Check if full rollover; code if partial.
- Type of Program (Box 5): 1 for private QTP, 2 for state QTP/ESA.
- Sign & Distribute: Payer signs Copy A; furnish Copy B by January 31.
For recipients: Compare Box 1 to qualified expenses (tuition, books, up to $10,000 K-12 in 2025); report excess earnings on Form 1040.
Understanding Boxes on IRS Form 1099-Q
The form’s six boxes provide snapshot data for tax prep—use Pub. 970 for calculations.
| Box | Description | 2025 Tax Tip |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Gross distribution | Total payout; subtract qualified expenses for tax-free portion. |
| 2 | Earnings | Taxable if > qualified expenses; 10% penalty applies. |
| 3 | Basis | Nontaxable return of contributions. |
| 4 | Rollover | Indicates tax-free transfer (e.g., to another 529 or Roth). |
| 5 | Program type | 2 for most 529s/ESAs; affects state tax rules. |
| 6 | Beneficiary TIN | Student’s ID; mismatches trigger backup withholding. |
FMV basis used; document expenses to avoid audits.
Tax Rules for 529 and Coverdell Distributions in 2025
Distributions are tax-free if used for qualified expenses; otherwise, earnings are income + 10% penalty (exceptions: scholarships, death/disability).
- Qualified Expenses: Tuition, fees, books, supplies, room/board (half-time+), computers; up to $10,000 K-12 tuition; apprenticeships; student loans ($10,000 lifetime).
- 2025 Updates: K-12 cap remains $10,000 (rises to $20,000 in 2026); new credentialing programs (WIOA-approved) from July 5, 2025; Roth rollovers up to $35,000 lifetime.
- Rollover Rules: Tax-free to another 529/ESA or ABLE; Roth transfers count as distributions but penalty-free.
- Gift Tax: Contributions up to $19,000/person ($38,000 couple) gift-tax free; superfund up to $95,000 over 5 years.
No double-dipping with credits like American Opportunity (coordinate via Form 8863). State taxes vary—check Pub. 970.
Common Mistakes with Form 1099-Q and How to Avoid Them
Errors can lead to IRS notices or overpayments—top issues for 2025:
- Misreporting Recipient: Using owner vs. beneficiary—check distribution type.
- Ignoring Box 2 Earnings: Assuming all tax-free—track expenses meticulously.
- Late Furnishing: Missing January 31—use e-delivery for proof.
- No Expense Matching: Forgetting receipts—use apps like Keeping.com.
- Rollover Oversights: Treating as taxable—check Box 4.
Consult Pub. 970; e-file reduces errors.
Penalties for Form 1099-Q Non-Compliance in 2025
Payers face steep fines; recipients risk underpayment penalties.
| Violation | Penalty (2025) |
|---|---|
| Late Filing/Furnishing | $60/form (timely), $120 (30+ days late), $310 (intentional); max $1,291,000/year. |
| Incorrect Info | Same as above; $630 intentional disregard. |
| Non-Qualified Withdrawal (Recipient) | 10% on earnings + income tax; exceptions apply. |
| Backup Withholding Failure | 24% on payments if TIN mismatch. |
Waivers for reasonable cause; first-time abatement available. E-filing mitigates risks.
IRS Form 1099-Q Download and Printable
Download and Print: IRS Form 1099-Q
Frequently Asked Questions About IRS Form 1099-Q
Do I owe taxes on all 1099-Q distributions?
No—only earnings exceeding qualified expenses; basis (Box 3) is always tax-free.
When is Form 1099-Q issued for 2025?
By January 31, 2026; access online via plan portals.
Can 529 funds roll over to a Roth IRA penalty-free?
Yes, up to $35,000 lifetime, subject to annual limits ($7,000 under 50).
What’s new for K-12 in 2025?
$10,000 cap; expands to credentialing post-July 5.
How do I report a non-qualified withdrawal?
On Form 1040, Schedule 1; penalty on Schedule 2.
For more, visit IRS.gov/Form1099Q or Pub. 970.
Final Thoughts: Navigate 1099-Q with Confidence for 2025 Education Savings
IRS Form 1099-Q demystifies 529 and Coverdell distributions, ensuring tax-free growth translates to real benefits amid 2025’s expansions like higher K-12 limits and Roth rollovers. With over $500 billion in assets, proper reporting safeguards your savings—download the April 2025 form from IRS.gov today and track expenses diligently. Consult a tax pro for personalized advice to avoid penalties and maximize deductions.
This article is informational only—not tax advice. Verify with IRS or a professional.