Table of Contents
IRS Form W-8IMY – Certificate of Foreign Intermediary, Foreign Flow-Through Entity, or Certain U.S. Branches for United States Tax Withholding and Reporting – In the complex world of international taxation, IRS Form W-8IMY plays a crucial role for foreign entities involved in U.S. income flows. Whether you’re a foreign intermediary, a flow-through entity like a partnership or trust, or a specific U.S. branch handling payments, understanding this form is essential to ensure compliance with U.S. tax withholding and reporting requirements. This guide breaks down everything you need to know about Form W-8IMY, including its purpose, who must file it, how to complete it, and recent updates as of 2025. By properly using this form, entities can avoid excessive withholding taxes and streamline reporting under sections like 1441, 1442, and 1446.
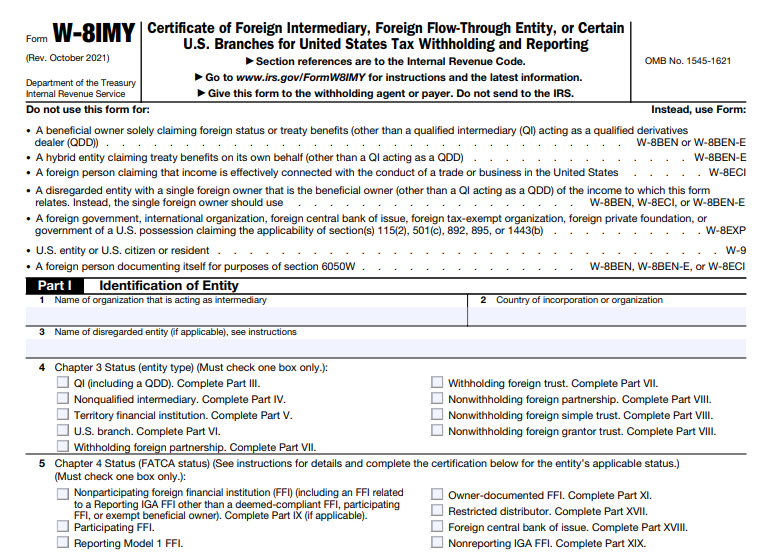
What is IRS Form W-8IMY?
IRS Form W-8IMY, officially titled “Certificate of Foreign Intermediary, Foreign Flow-Through Entity, or Certain U.S. Branches for United States Tax Withholding and Reporting,” is a certification document used to establish the foreign status of certain entities for U.S. tax purposes. Unlike other W-8 forms (such as W-8BEN for individuals or W-8BEN-E for entities claiming treaty benefits), Form W-8IMY is specifically for intermediaries or pass-through structures that receive U.S.-sourced income on behalf of others.
The form helps withholding agents (like U.S. financial institutions or payers) determine the correct withholding tax rate on payments such as dividends, interest, or proceeds from asset sales. It supports compliance with Chapter 3 (withholding on foreign persons) and Chapter 4 (FATCA) of the Internal Revenue Code, including provisions for publicly traded partnership (PTP) distributions and transfers under section 1446(f). Essentially, it allows the entity to “pass through” tax documentation from underlying beneficial owners, ensuring accurate tax treatment without the intermediary being treated as the ultimate payee.
Key features include:
- Certifications for entity status (e.g., qualified intermediary (QI), nonqualified intermediary (NQI)).
- Requirements for attaching withholding statements that allocate income to specific pools or owners.
- Integration with FATCA for global information exchange.
Failing to provide a valid Form W-8IMY can result in a default 30% withholding tax on U.S.-sourced income, making it vital for cross-border financial operations.
Who Needs to File Form W-8IMY?
Form W-8IMY is required for specific foreign entities and U.S. branches acting in an intermediary capacity. You should use this form if you are:
- Foreign Intermediaries: Such as qualified intermediaries (QIs) or nonqualified intermediaries (NQIs) that receive payments on behalf of beneficial owners.
- Foreign Flow-Through Entities: Including foreign partnerships, simple trusts, or grantor trusts that pass income to partners, beneficiaries, or owners.
- Certain U.S. Branches: U.S. branches of foreign banks or insurance companies treated as U.S. persons for withholding purposes, or those transmitting documentation for payees.
- Territory Financial Institutions: Organized under U.S. territory laws and agreeing to U.S. person status for Chapters 3 and 4.
- Qualified Securities Lenders (QSLs) or Qualified Derivatives Dealers (QDDs): For handling substitute dividends or derivatives.
Do not use this form if you’re a beneficial owner claiming foreign status or treaty benefits directly—opt for W-8BEN or W-8BEN-E instead. Entities must provide the form to the withholding agent or payer (not directly to the IRS) before receiving reportable amounts or withholdable payments. It’s typically valid for three years from the signature date, unless circumstances change.
How to Fill Out IRS Form W-8IMY: Step-by-Step Guide
Completing Form W-8IMY requires careful attention to detail, as it involves multiple parts based on your entity’s status. Always refer to the official IRS instructions for the most accurate guidance. Here’s a high-level overview:
- Part I: Identification of Entity
- Enter your entity’s name, country of incorporation, and disregarded entity details if applicable.
- Check your Chapter 3 status (e.g., QI, NQI, withholding foreign partnership).
- Provide your permanent residence address, mailing address, and tax identification numbers (e.g., GIIN for FATCA-registered entities, EIN if required).
- Include any reference information for associating with other certificates.
- Part II: Disregarded Entity or Branch Receiving Payment (if applicable)
- Complete if you’re a disregarded entity with its own GIIN or a branch in a different jurisdiction.
- Parts III-VIII: Chapter 3 Status Certifications
- Select and complete only one relevant part:
- Part III: Qualified Intermediary – Certify QI status and assumptions of withholding responsibilities.
- Part IV: Nonqualified Intermediary – Certify transmission of documentation and withholding statements.
- Part V: Territory Financial Institution – Agree to U.S. person treatment or provide statements.
- Part VI: Certain U.S. Branches – Certify non-ECI income handling.
- Part VII: Withholding Foreign Partnership or Trust – Assume primary withholding duties.
- Part VIII: Nonwithholding Foreign Partnership, Simple Trust, or Grantor Trust – Provide statements for pass-through income.
- Select and complete only one relevant part:
- Parts IX-XXVIII: Chapter 4 (FATCA) Status (if receiving withholdable payments)
- Check the appropriate box from Part I Line 5 and complete the corresponding certification (e.g., sponsored FFI, active NFFE).
- Part XXIX: Certification
- Sign under penalties of perjury, confirming accuracy and agreeing to notify of changes within 30 days.
Attach a withholding statement detailing income allocations, beneficial owners, and applicable rates. Electronic signatures are permitted if compliant with regulations.
For visual reference, here’s a sample of a filled-out Form W-8IMY:
Common pitfalls include incomplete withholding statements or mismatched certifications—use automation tools for accuracy if managing high volumes.
Key Certifications and Requirements for Form W-8IMY
Form W-8IMY emphasizes certifications to ensure proper tax treatment:
| Certification Type | Description | Applicability |
|---|---|---|
| Chapter 3 Status | Confirms role as QI, NQI, etc., and withholding assumptions (e.g., primary under section 1446(f)). | All filers. |
| Chapter 4 (FATCA) Status | Includes GIIN for participating FFIs or deemed-compliant entities. | Entities receiving withholdable payments. |
| Withholding Statement | Allocates payments to pools (e.g., U.S. payees, exempt owners) with supporting docs like W-8 or W-9. | Intermediaries and flow-throughs. |
| QDD/QSL Specifics | Certifies compliance for derivatives or securities lending. | Specialized dealers/lenders. |
| Treaty Benefits | Passed through via attached statements, not claimed directly on the form. | Hybrid entities or owners. |
Entities must renew the form upon expiration or changes, and provide it before payments to avoid 30% default withholding.
IRS Form W-8IMY Download and Printable
Download and Print: IRS Form W-8IMY
Recent Updates to IRS Form W-8IMY in 2025
As of 2025, the current revision of Form W-8IMY remains October 2021, with no major updates announced since then. Key changes from the 2021 revision include:
- Enhanced provisions for section 1446(f) withholding on PTP interest transfers (effective from 2023).
- Updates for qualified securities lenders (QSLs) with transition relief through 2022.
- Additions for alternative withholding statements and beneficial owner verification.
- Integration with section 6050Y for life insurance reporting.
- Requirements for foreign TINs (FTINs) for QDDs and electronic signature allowances.
These updates aim to improve compliance with FATCA and withholding on partnership interests. Filers should check the IRS website for any interim guidance or future revisions.
Common Challenges and Tips for Managing Form W-8IMY
Handling Form W-8IMY can be tricky due to:
- Non-standardized withholding statements leading to errors.
- Complex data for multiple income types and beneficiaries.
- High manual processing times and compliance risks.
Tips:
- Use AI-powered tools for data extraction and validation.
- Maintain an audit trail for IRS reviews.
- Consult tax professionals for entity-specific advice.
- Stay updated via IRS newsletters or trusted advisors like PwC or KPMG.
FAQs About IRS Form W-8IMY
What is the difference between W-8IMY and W-8BEN-E?
W-8IMY is for intermediaries passing through income, while W-8BEN-E is for entities claiming treaty benefits directly.
How long is Form W-8IMY valid?
Generally three years, but renew sooner if circumstances change.
Can I submit Form W-8IMY electronically?
Yes, if the withholding agent accepts electronic submissions and signatures comply with rules.
What happens if I don’t provide Form W-8IMY?
Payments may face 30% withholding, and you could incur penalties for non-compliance.
Conclusion
IRS Form W-8IMY is indispensable for foreign intermediaries and flow-through entities navigating U.S. tax withholding. By understanding its requirements and staying compliant, you can minimize tax burdens and avoid penalties. For personalized guidance, consult a tax expert or visit the official IRS resources. Remember, accurate completion ensures smooth international financial transactions in 2025 and beyond.